On May 12, Speaker Pelosi introduced H.R. 6800, the Health and Economic Recovery Omnibus Emergency Solutions Act, or the HEROES Act, in the House of Representatives, which serves as a blueprint for the next round of federal stimulus funding.
The House passed this bill on May 15. And we must ensure that the Senate takes up this bill, or introduces their own, so that these funds become a reality for those who need it most.
This bill provides nearly $3 trillion for an array of programs and sectors, including additional funding for the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) as well as for individuals, businesses, states, and local governments.
We are pleased that the HEROES Act includes housing advocates’ three priorities:
- $11.5 billion for Emergency Solutions Grants (ESG)
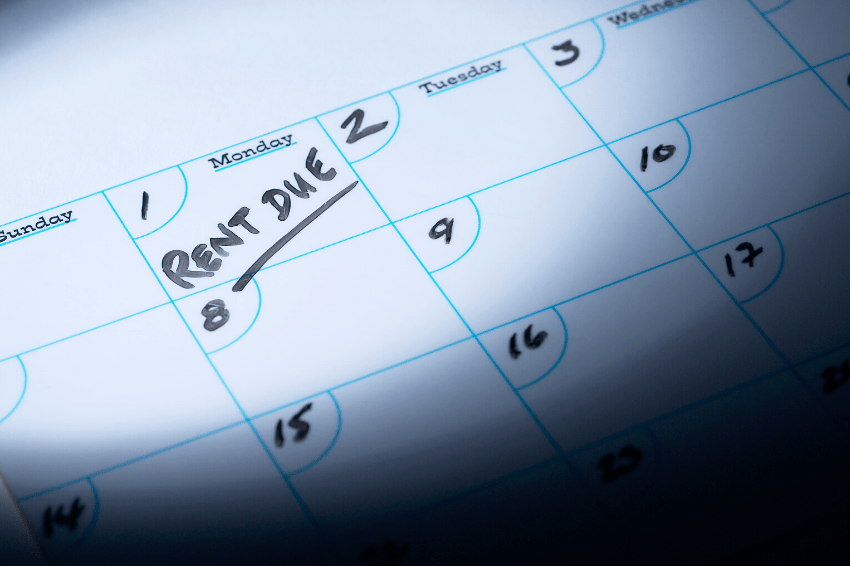
- $100 billion for Emergency Rental Assistance and Eviction Prevention
- A national, uniform moratorium on evictions and foreclosures
Members of Congress need to hear that people experiencing and at-risk of homelessness and homeless response organizations require this additional funding to address the needs created by the coronavirus pandemic, including preventing homelessness and housing instability through rental assistance and stemming the tide of evictions and foreclosures.
THE BREAKDOWN
A more detailed summary can be found here.
Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
- Emergency Rental Assistance – $100 billion to provide emergency assistance to help low-income renters at risk of homelessness avoid eviction due to the economic impact of the coronavirus pandemic.
- Homeless Assistance Grants – $11.5 billion for Emergency Solutions Grants to address the impact of coronavirus among individuals and families who are homeless or at risk of homelessness and to support additional homeless assistance, prevention, and diversion activities to mitigate the impacts of the pandemic.
- Community Development Block Grant – $5 billion for coronavirus response and to mitigate the impacts in our communities to be distributed by formula to current grantees. The legislation continues to waive the public services cap to allow communities to respond to the impacts of the pandemic.
- Tenant-Based Rental Assistance – $4 billion to allow public housing agencies (PHAs) to respond to coronavirus and the ability to keep over 2.2 million families stably-housed even when facing a loss of income, including:
- $1 billion for new, temporary, vouchers for individuals and families who are homeless or at risk of becoming homeless, or fleeing domestic violence.
- Allows PHAs the flexibility necessary for the safe and effective administration of these funds while maintaining fair housing, nondiscrimination, labor standards, and environmental protections.
- Public Housing Operating Fund – $2 billion for PHAs to carry out coronavirus response for the operation and management of almost 1 million public housing units. Allows PHAs the flexibility necessary for the safe and effective administration of these funds while maintaining fair housing, nondiscrimination, labor standards, and environmental protections.
- Housing for Persons with AIDS – $15 million to maintain operations, rental assistance, supportive services, and other necessary actions to mitigate the impact of coronavirus on low-income persons with HIV/AIDS.
- Project-Based Rental Assistance – $750 million to ensure the continuation of housing assistance for low-income individuals and families living in project-based rental assistance properties, and to ensure housing providers can take the necessary actions to prevent, prepare for, and respond to the pandemic.
- Housing for the Elderly – $500 million to maintain operations at properties providing affordable housing for low-income seniors and to ensure housing providers can take the necessary actions to prevent, prepare for, and respond to the coronavirus pandemic. To ensure access to supportive services for this vulnerable population, this includes $300 million for service coordinators and the continuation of existing congregate service grants for residents of assisted housing projects.
- Housing for Persons with Disabilities – $200 million to maintain operations at properties providing affordable housing for low-income persons with disabilities, and to ensure housing providers can take the necessary actions to prevent, prepare for, and respond to the coronavirus pandemic.
- Housing Counseling Assistance – $100 million to enable housing counselors to respond to the surge of demand for services, which include foreclosure and eviction mitigation counseling, in light of the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The bill allows the purchase of technology and equipment so services can be provided through electronic means.
- Office of Fair Housing and Equal Opportunity – $14 million to address fair housing issues resulting from coronavirus. This includes:
- $4 million for Fair Housing Organization Initiative grants
- $10 million for Education and Outreach grants to educate the public and the housing industry about fair housing rights and responsibilities during the COVID-19 pandemic
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
- $1.3 billion to FEMA to prevent, prepare for, and respond to coronavirus
- Eliminates requirement of 25% share-of-cost; covers 100% of disaster-related costs
- $200 million for the Emergency Food and Shelter Program
Relief to Local, State, and Tribal Governments
- State Fiscal Relief – $500 billion in funding to assist state governments with the fiscal impacts from the public health emergency caused by the coronavirus.
- Local Fiscal Relief – $375 billion in funding to assist local governments with the fiscal impacts from the public health emergency caused by the coronavirus.
- Tribal Fiscal Relief – $20 billion in funding to assist Tribal governments with the fiscal impacts from the public health emergency caused by the coronavirus.
- Fiscal Relief for Territories – $20 billion in funding to assist governments of the Territories with the fiscal impacts from the public health emergency caused by the coronavirus.
- Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFI) – $1 billion for economic support and recovery in distressed communities by providing financial and technical assistance to CDFIs.
Relief to Individuals and Homeowners
- Tax Credit Implementation – $599 million for implementation of additional payments to individuals. The income limits are the same as in the CARES Act.
- $1,200 ($2,400 in the case of a joint return) plus
- $1,200 per dependent (with a maximum of 3)
- Assistance to Homeowners – $75 billion to states, territories, and tribes to address the ongoing needs of homeowners struggling to afford their housing due directly or indirectly to the impacts of the pandemic by providing direct assistance with mortgage payments, property taxes, property insurance, utilities, and other housing related costs.
Relief to Small Businesses
- Assisting Small Businesses – $10 billion in grants to small businesses that have suffered financial losses as a result of the coronavirus outbreak.
Food, Child Care, and Family Assistance Programs
- Administration for Children and Families – $10.1 billion to provide supportive and social services for families and children through programs including:
- $1.5 billion for the Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP)
- $1.5 billion to support paying water bills for low income families
- $50 million for Family Violence Prevention and Services
- Administration for Community Living – $100 million to provide direct services such as home-delivered and prepackaged meals, and supportive services for seniors and disabled individuals, and their caregivers.
- Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) – Provides $10 billion to support anticipated increases in participation and to cover program cost increases related to flexibilities provided to SNAP by the Families First Coronavirus Response Act.
- Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women Infants and Children (WIC) – Provides an additional $1.1 billion to provide access to nutritious foods to low-income pregnant women or mothers with young children who lose their jobs or are laid off due to the COVID-19 emergency.
- The Emergency Food Assistance Program (TEFAP) – Includes $150 million to help local food banks meet increased demand for low-income Americans during the emergency.
- Child Nutrition Programs – Includes $3 billion in additional funding to provide emergency financial relief to school meal providers and USDA’s Child and Adult Care Food Program.
- Second Chance Act grants – $250 million for grants to help facilitate the reintegration of ex-prisoners back into society and to prevent recidivism.